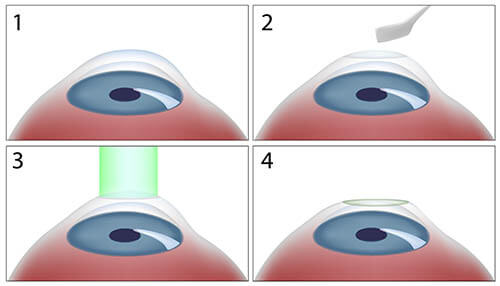
What to Expect During the PRK Procedure
At ADV Vision, PRK is performed using state-of-the-art technology to enhance precision and comfort:
- Surface Cell Removal
- After applying anesthetic eye drops, the outer layer of the cornea (epithelium) is gently removed using a special brush.
- Laser Vision Correction
- A cool excimer laser is then used to reshape the corneal tissue, correcting your refractive error to improve vision.
- Healing Enhancement
- A sponge soaked in Mitomycin-C is placed briefly on the cornea to minimize haze and support proper healing.
- Bandage Contact Lens Placement
- A soft contact lens acts as a protective bandage and is worn for 5–7 days to aid comfort and promote surface cell regrowth.
PRK Recovery Timeline
- Day 1–3: Initial vision may be functional but slightly blurry or fuzzy
- Week 1: Vision typically worsens as the surface cells regenerate
- Week 2–6: Gradual improvement as the cornea smooths and refocuses light properly
- Month 1–3: Maximum visual clarity is often achieved within 1 to 3 months
During recovery, patients may experience:
- Mild burning, stinging, or tearing
- Temporary light sensitivity
- Rarely, moderate to severe discomfort, which is managed with medicated drops and the bandage lens
You’ll receive comfort drops (mild topical anesthetic), as well as antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and steroid eye drops to support healing.
Follow-Up Care After PRK
- Day-After Checkup: To ensure early healing is progressing well
- Day 4–6 Visit: Bandage lens removal and vision reassessment
Your eye surgeon will continue to monitor your progress and adjust medications as needed during your recovery.
Is PRK Right for You?
PRK is an excellent vision correction option if you:
- Have thin or irregular corneas
- Lead an active lifestyle where a LASIK flap may pose risks
- Were previously told you’re not a good candidate for LASIK
ADV Vision Centers proudly offers PRK surgery at our locations in Paso Robles, Santa Maria, and San Luis Obispo.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)